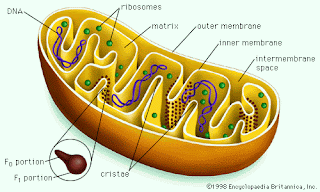
Microbodies
These are single layered membranous sac like structures formed from the vesicles of endoplasmic reticulum or golgi bodies. These are - Peroxisomes or Glyoxisomes . Peroxisomes Peroxisomes are formed from pre-existing peroxisomes. These are found in plants showing “Photorespiration” (C -3 plants). Peroxisomes participate in the process of photorespiration along with choloplast and mitochondria.In peroxisome oxidation of glycolic acid (produced in chloroplast in photorespiration) occurs. These are also found in animal cells like “Protozoons” residing in liver or kidney cells. In peroxisomes ,catalases,oxidases enzymes are present. These enzymes assist degradation of toxic materials in cells. Peroxisomes invole in fat-metabolism in animal cells. Glyoxisomes These are also single layered membrane bound spherical bodies found in cell showing “ Glyoxylate cycle ” Enzymes of glyoxisomes participate in...